The private 5G market offers many opportunities for companies and industrialists, and this market is expected to achieve a significant growth over the next few years due to the strong demand for high-quality connectivity solutions and reduced latency.

In the field of industry and smart cities, a number of players are interested in private 5G. Globally, the private 5G market is rapidly expanding due to the rapid growth of industrial and commercial applications requiring high-quality connectivity and reduced latency. Private 5G offers dedicated, secure and flexible connectivity for businesses and industries, allowing them to enjoy 5G speed and reliability without having to connect to a public network.
The main industries subject to the private 5G are automated factories, smart warehouses, intelligent transportation systems, health and medical care, mining, etc.
Let’s take the time to understand what a private network is and how this network will technically contribute to the transformation of uses in the industry and in large public complexes (stations, airports, concert halls, etc.).
What is a private mobile network ?
Private mobile networks1 (PMN) are different than mobile networks open to the general public, and are used by companies (airports, stations, stadiums, motorways, etc.) and public services (local authorities, etc.) on a given geographical footprint (local, regional or national) for their critical and non-critical communications. These companies want their communications to pass through a high-performance network (in terms of quality of service, capacity, security and availability).
The origins of PMN: from narrowband PMR2 to private 5G …
PMN initially centered around Wifi and voice uses of PTT:
Up to the early 2010’s, private networks were limited to WIFI, a wireless connectivity technology widely deployed in
offices, but mostly to narrowband PMR networks.
Those networks rely on disparate technologies that have not evolved much (TETRA, DMR, etc.). These solutions have been very successful in the past but no longer meet the needs of today’s users :
- They are generally limited to a PTT3 (Push to talk) voice service of the walkie-talkie type, and sometimes a short messaging service;
- The number of enabled devices is limited;
- They are often expensive to maintain.
The rise of PMN with the arrival of 4G then 5G :
To meet new demands for high bandwidth multimedia services, the ecosystem has moved towards 4G and is now preparing to migrate to 5G.
As a matter of fact, 4G/5G technologies offer several advantages over narrowband PMR technologies:
- Service quality management (prioritization and preemption for the most critical flows)
- 3GPP standardized technologies
- Improved security of trade and infrastructure
- Management of Internet of Things communications (IoT is one of the challenges of industry 4.0)
- Reduction of costs because they are
Each player seeking to enter the private mobile network market, alone or in partnership with other players, offers various solutions to meet the needs of companies and their uses. For example, Orange now offers companies, through its subsidiary Orange Business Services, its own range of “Mobile Private Networks” offers, with three different technical solutions (https://reseaux.orangebusiness. com/solutions/mobile-private-networks/):
- Mobile Virtual Private Network, a virtual private network using the Orange network. Radio access is managed by base stations deployed by Orange with guaranteed minimum bandwidth and customized coverage. The network core used also belongs to Orange.
- Mobile hybrid Private Network, a hybrid private network that relies on both Orange’s network equipment and customer-specific equipment on its site to maintain its data on campus.
- Standalone Mobile Private Network, a fully dedicated private network (including frequencies and core network) for the customer on their site.
Features and benefits of private 5G
5G technology represents a real opportunity for the private mobile network market. It was designed to address professional uses.
- A user with a 5G enabled device and a Mobile 5G offer could eventually benefit from a throughput of 10 Gbps in reception. Today, 5G (3.5 Ghz band) already allows to reach up to 1 Gbps of throughput in reception (up to 10 times more than 4G).
- The other benefit of 5G for businesses is responsiveness with latency (response time) that goes from 10 ms to 1 ms.
- The last major promise of 5G is the ultra-connectivity allowing a higher density of connected devices per km². The 5G will be able to support 1 million devices per km², a density of connection multiplied by 10 compared to 4G. 5G will allow the IoT market to continue to expand.
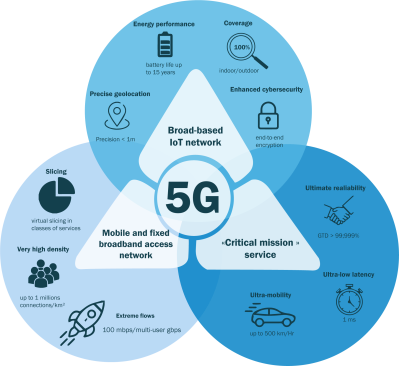
Network slicing to open new use cases
Unlike 4G, Private 5G allows you to benefit from the «E2E network slicing» functionality, which is the slicing of the end to-end network.
On the same private 5G network, the "E2E network slicing" allows to create different classes of services to which different priority levels can be assigned to better meet the specific needs of certain uses (in terms of bandwidth, latency, etc.). In this way, it will be possible to keep a network slice for uses such as critical communications or a very high level of security.

Source : Nokia
Operators accelerating and investing in 5G Standalone
There are two modes in 5G: NSA mode (non standalone) and SA mode (standalone). The 5G NSA is the one that has been put into service in priority by the majority of operators all over the world in order to set it up quickly and limit investments. The main objective is to provide higher bandwidth than 4G. From an architecture point of view, the 5G NSA uses the same existing 4G network core, while the antennas are 5G.
However, the long-term purpose of 5G is “the transformation of industry, services and mobility that it aims to enable said4” In France, the deployment of the 5G SA began in 2023. The majority of operators all over the world are preoccupied by this transition to 5G SA because it involves transforming all components of the network including the core of the network. This important deployment will be progressive, incremental and time-consuming.
Regulators need to open more frequencies to meet the rising of 5G
The growth of the private mobile network market will be more important if access to dedicated frequency bands is facilitated by telecom regulators.
While it is possible for companies to meet part of their needs by subscribing to commercial mobile operators, the deployment of private mobile networks may require access to dedicated frequency bands for, for example, limiting the risk of interference or congestion. In France, ARCEP opened a frequency allocation window for 4G in 2019 for 2.6 Ghz band (band 38) in TDD mode (with a bandwidth of 2x20 Mhz). For access to 5G private networks, ARCEP offers the following bands:
- The band spectrum from 3.800 Ghz to 4.000 GHz (a 5G test window in this band is open by ARCEP until 31 December 20235)
- Millimeter bands: 26 GHz
- 2.6 Ghz TDD band, originally planned for 4G, could also be used for 5G
The development of private mobile networks on a 5G technology basis will better meet the growing need for connectivity from companies that have higher coverage, bandwidth and security requirements. This is the case, for example, for a company that has a large industrial campus and needs reliable and efficient connectivity both in-buildings and outdoor.
According to GlobeNewswire, the global market size of private 5G networks is expected to grow by more than 42.4% and reach a market value of around USD 31,589 million by 2030. The private 5G network is a real catalyst for the fourth industrial revolution and a necessary investment choice for companies and large institutions.
1PMN : Private/Professional Mobile Network (in french : Réseau Mobile Privée/Professionnel ou RMP)
2PMR : Private/Professional Mobile Radio
3PTT: Push To Talk - voice service to make a group call without the need to dial a number. Just press a button and talk to reach multiple predefined recipients simultaneously.
4Report of l’Académie des sciences, « Report on 5G and mobile communications networks »
5https://www.arcep.fr/demarches-et-services/professionnels/transformation-numerique-des-entreprises/plateformes-experimentation-5g-bande-38-40-ghz.html